
History of Banking in India | Banking Sector History of India
History of Banking in India:- The financial sector in India serves as the foundation for the country’s economic growth. As technology has advanced, the banking system and management have undergone significant transformations in response to customer demands.
The history of Indian banking, which dates back to before India gained independence in 1947, is one of the most frequently asked questions on a variety of government exams. The development of India’s banking industry will be the subject of an in-depth discussion in this article.
There are three phases to the development of the banking industry:
-
Phase 1: The Initial Period, which began in 1770 and ended in 1969 Phase.
-
Phase II: From 1969 to 1991, there was a period of nationalization.
-
Phase III: The Banking Sector Reforms or Liberalization Phase, which began in 1991 and continues to thrive today.
An illustration of how the Indian banking system has changed over time is provided below:
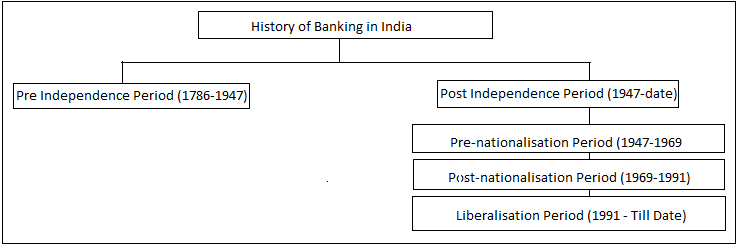
Candidates can learn more about the functions of banks in the linked article. History of Banking in India
The various stages of the evolution of the banking industry will be discussed further down in this article.
Pre-Independence Period (1786-1947)
The “Bank of Hindustan,” which was established in 1770 and was situated in the then-Indian capital of Calcutta, was India’s first bank during the pre-independence period (1786-1947). However, in 1832, this bank failed and ceased operations.
Over 600 banks were registered in the nation prior to independence, but only a few of them survived.
In India, a number of other banks followed in the footsteps of the Bank of Hindustan. They included
- The General Bank of India, founded in 1786
- Oudh Commercial Bank, founded in 1881
- the Bank of Bengal, founded in 1809
- the Bank of Bombay, founded in 1840
- the Bank of Madras, founded in 1843
During the time that the British ruled India, The East India Company established three banks: The Presidential Banks were the Bank of Bombay, the Bank of Madras, and the Bank of Bengal. In 1921, these three banks merged into a single entity known as the “Imperial Bank of India.“
The State Bank of India, which is currently the largest public sector bank, took over the Imperial Bank of India after it was nationalized in 1955.
The following is a list of additional banks that were established prior to independence.
|
Pre-Independence Banks in India |
|
| Bank Name | Year of Establishment |
| Allahabad Bank | 1865 |
| Punjab National Bank | 1894 |
| Bank of India | 1906 |
| Central Bank of India | 1911 |
| Canara Bank | 1906 |
| Bank of Baroda | 1908 |
If we examine the factors that contributed to the demise of numerous major banks prior to independence, the following conclusions can be reached:
-
Indian account holders were more likely to commit fraud.
-
a lack of technology and machines.
-
Time-consuming and human errors.
-
fewer establishments
-
inadequate management abilities.
The post-independence era followed the pre-independence era, which saw significant shifts in the banking industry’s landscape and has since progressed significantly.
Post-Independence Period (1947-1991)
When India gained independence, all of the country’s major banks were privately run, which was concerning because rural residents still relied on money lenders for financial assistance.
The government at the time made the decision to nationalize the banks in an effort to resolve this issue. The Banking Regulation Act of 1949 authorized the nationalization of these banks. In contrast, the Reserve Bank of India was nationalized in 1949.
Candidates can view the list of acts and reforms affecting the banking sector in the linked article.
The State Bank of India was established in 1955, and the remaining fourteen banks were nationalized between 1969 and 1991. These were the financial institutions with national deposits of more than fifty crores.
History of Banking in India 2023
The following is a list of the 14 banks that were nationalized in 1969:
-
Allahabad Bank
-
Bank of India
-
Bank of Baroda
-
Bank of Maharashtra
-
Central Bank of India
-
Canara Bank
-
Dena Bank
-
Indian Overseas Bank
-
Indian Bank
-
Punjab National Bank
-
Syndicate Bank
-
Union Bank of India
-
United Bank
-
UCO Bank
Six more banks were nationalized in 1980, bringing the total to 20. Among these banks were:
- Andhra Bank
- Corporation Bank
- New Bank of India
- Oriental Bank of Comm.
- Punjab & Sind Bank
- Vijaya Bank
In addition to the 20 banks mentioned above, seven SBI subsidiaries were nationalized in 1959:
- State Bank of Patiala
- State Bank of Hyderabad
- State Bank of Bikaner & Jaipur
- State Bank of Mysore
- State Bank of Travancore
- State Bank of Saurashtra
- State Bank of Indore
Except for the State Bank of Saurashtra, which merged in 2008, and the State Bank of Indore, which merged in 2010, all of these banks later merged with the State Bank of India in 2017.
Note: In 1975, India established the Regional Rural Banks for the purpose of developing India’s rural areas. The list of RRBs in India can be found in the linked article.
Impact of Nationalisation
The Government decided to nationalize the banks for a variety of reasons. The effects of nationalizing Indian banks are as follows:
-
This resulted in an increase in funds, improving the country’s economic situation.
-
increased productivity.
-
aided in boosting the country’s rural and agricultural sectors.
-
It provided the populace with a significant opportunity for employment.
-
Bank profits were used by the government to improve the lives of the people.
-
There was less competition, which made work more efficient.
This period following India’s independence was the one that saw significant advancements in the banking sector and its evolution.
Liberalisation Period (1991-Till Date)
To maintain the profits generated by the banking sector, regular regulations and monitoring must be adhered to once banks have been established in the country. A significant part of the banking sector’s development is played by the final or ongoing phase.
The government decided to establish a committee led by Shri in order to offer the Nationalized Public Sector Banks stability and profitability. M Narasimham to oversee the various banking industry reforms.
The most significant development in India was the establishment of private sector banks. Ten private sector banks were granted permission to establish themselves in the country by the RBI. Among these banks were:
- Global Trust Bank
- ICICI Bank
- HDFC Bank
- Axis Bank
- Bank of Punjab
- IndusInd Bank
- Centurion Bank
- IDBI Bank
- Times Bank
- Development Credit Bank
The following are additional steps taken:
-
establishment of various foreign bank branches in India.
-
Bank nationalization could not continue.
-
The committee made the announcement that the government and the RBI would treat banks in the public and private sectors alike.
-
Joint ventures with Indian banks could be started by any foreign bank.
-
With the advancement of banking and technology, payment banks were established.
-
Small finance banks were given permission to open branches throughout India.
-
With the availability of apps for fund transfers and internet banking, a significant portion of Indian banking moved online.
As a result, India’s banking history demonstrates that, in response to changing customer demands and the passage of time, significant changes have been made to the banking industry in an effort to boost growth.
———————————————————- The End —————————————————–
www.GKDuniya.in will update many more new jobs and study materials and exam updates, keep Visiting and share our post of Gkduniya.in, So more people will get this. This content and notes are not related to www.GKDuniya.in and if you have any objection over this post, content, links, and notes, you can mail us at gkduniyacomplaintbox@gmail.com And you can follow and subscribe to other social platforms. All social site links are in the subscribe tab and bottom of the page.
Important Links
Official Links ———————————————————- Related Links
You-tube ———————————————————- GKDuniya9
Instagram ———————————————————- GKDuniya.in
Facebook ———————————————————- GKDuniya.in
Twitter ———————————————————- GKDuniya.in
Linkedin ———————————————————- GKDuniya.in
Pinterest ———————————————————- GKDuniya.in
Google Rank ———————————————————- Gkduniya
Tags:- history of indian banking system pdf, history of banking in india ppt, history of banking system in india, history of banking in india (rbi), history of banking pdf, history of banking in world, evolution of banking in india wikipedia, indian banking system notes, history of indian banking system pdf, history of banking in india ppt, history of banking pdf, history of banking in world, history of banking in india (rbi), evolution of banking in india wikipedia, indian banking system notes, banking in india pdf, history of indian banking system, history of banking in india pdf, history of banking pdf, history of banking in the world ppt, history of banking ppt, banking system in india ppt free download, growth of banking sector in india ppt, banking sector ppt free download, conclusion of history of banking in india,

