
Indian History ll Ancient History ll Medieval History ll Freedom Struggle
[google-translator]
Indian History:- India’s set of experiences and culture is dynamic, traversing back to the start of human civilization. It starts with a baffling society along the Indus River and in cultivating networks in the southern terrains of India.
The historical backdrop of India is interspersed by steady combination of relocating individuals with the different societies that encompass India. Accessible proof proposes that the utilization of iron, copper and different metals was broadly predominant in the Indian sub-landmass at a genuinely early period, which is demonstrative of the advancement that this piece of the world had made. Before the finish of the fourth thousand years BC, India had arisen as a district of profoundly created human progress.
The Indus Valley Civilization (indian history)
The History of India starts with the introduction of the Indus Valley Civilization, all the more definitely known as Harappan Civilization. It prospered around 2,500 BC, in the western piece of South Asia, what today is Pakistan and Western India. The Indus Valley was home to the biggest of the four antiquated metropolitan civic establishments of Egypt, Mesopotamia, India and China. Nothing was thought about this civilization till 1920s when the Archeological Department of India completed unearthings in the Indus valley wherein the vestiges of the two old urban communities, viz. Mohenjodaro and Harappa were uncovered. The remains of structures and different things like family unit articles, weapons of war, gold and silver trimmings, seals, toys, stoneware products, and so forth, show that exactly four to 5,000 years prior an exceptionally evolved Civilization thrived in this area.
The Indus valley progress was essentially a metropolitan civilization and individuals lived in all around arranged and very much constructed towns, which were likewise the communities for exchange. The remnants of Mohenjodaro and Harappa show that these were heavenly shipper urban areas all around arranged, experimentally laid, and very much took care of. They had wide streets and an all around created waste framework. The houses were made of prepared blocks and had at least two stories.
The exceptionally acculturated Harappans knew the craft of developing cereals, and wheat and grain comprised their staple food. They burned-through vegetables and products of the soil sheep, pork and eggs too. Confirmations show that they wore cotton just as woolen articles of clothing. By 1500 BC, the Harappan culture reached a conclusion. Among different causes credited to the rot of Indus Valley Civilization are the repetitive floods and other common causes like seismic tremor, and so forth.

Vedic Civilization (indian history)
The Vedic civilization is the soonest human advancement throughout the entire existence of old India. It is named after the Vedas, the early writing of the Hindu public. The Vedic Civilization prospered along the stream Saraswati, in an area that currently comprises of the cutting edge Indian conditions of Haryana and Punjab. Vedic is inseparable from Hinduism, which is another name for strict and otherworldly imagined that has advanced from the Vedas.
The Ramayana and Mahabharata were the two extraordinary stories of this period.


The Buddhist Era
During the existence season of Lord Gautam Buddha, sixteen incredible forces (Mahajanpadas) existed in the seventh and mid sixth hundreds of years BC. Among the more significant republics were the Sakyas of Kapilavastu and the Licchavis of Vaishali. Other than the republics, there were monarchical states, among which the significant ones were Kaushambi (Vatsa), Magadha, Kosala and Avanti. These states were governed by fiery characters who had set out upon the approaches of glorification and assimilation of adjoining states. Be that as it may, there were particular indications of the conservative states while those under the rulers were extending.
Buddha was brought into the world in BC 560 and passed on at eighty years old in BC 480. The spot of his introduction to the world was a forest known as Lumbini, close to the city of Kapilavastu, at the foot of Mount Palpa in the Himalayan reaches inside Nepal. Buddha, whose unique name was Siddhartha Gautama, was the author of Buddhism, the religion and the philosophical framework that advanced into an incredible culture all through quite a bit of southern and eastern Asia.


Alexander’s Invasion
In 326 BC, Alexander attacked India, subsequent to intersection the stream Indus he progressed towards Taxila. He at that point tested lord Porus , leader of the realm between the waterways Jhelum and Chenab. The Indians were vanquished in the savage fight, despite the fact that they battled with elephants, which the Macedonians had at no other time seen. Alexander caught Porus and, similar to the next neighborhood rulers he had vanquished, permitted him to keep on overseeing his region.
During this outing to streams Hydaspes and Indus in the south, Alexander searched out the Indian savants, the Brahmins, who were acclaimed for their shrewdness, and bantered with them on philosophical issues. He got incredible for quite a long time in India for being both, a savvy thinker and a daring champion.
One of the towns in which the military ended had a place with the Mallis, who were supposed to be quite possibly the most warlike of the Indian clans. Alexander was injured a few times in this assault, most truly when a bolt penetrated his breastplate and his ribcage. The Macedonian officials saved him in a near disaster from the town.
Alexander and his military arrived at the mouth of the Indus in July 325 BC, and turned toward the west for home.


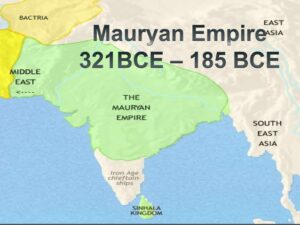
The Mauryan Empire
The time of the Mauryan Empire (322 BC-185 BC) denoted another age throughout the entire existence of India. It is supposed to be a period when sequence got unequivocal. It was a period when legislative issues, workmanship, exchange and business raised India to a sublime stature. It was a time of unification of the domains which lay as divided realms. In addition, Indian contact with the rest of the world was set up successfully during this period.
The disarray following the passing of Alexander allowed Chandragupta Maurya a chance to free the nations from the burden of the Greeks, and accordingly involve the areas of Punjab and Sindh. He later toppled the force of Nandas at Magadha with the guide of Kautilya, and established a sublime Mauryan domain in 322 BC. Chandragupta, who administered from 324 to 301 BC, consequently, acquired the title of deliverer and the primary sovereign of Bharata.
At a higher age, Chandragupta got intrigued by religion and left his seat to his child Bindusar in 301 BC. Bindusar vanquished the Highland of Deccan during his rule of 28 years and gave his seat to his child Ashoka in 273 BC. Ashoka arose not just as the most renowned lord of the Maurya administration, but at the same time is viewed as one of the best ruler of India and the world.
His domain covered the entire region from Hindu Kush to Bengal and reached out over Afghanistan, Baluchistan and the entire of India except for a little zone in the farthest south. The valleys of Nepal and Kashmir were additionally remembered for his domain.
The main occasion of Ashoka’s rule was the success of Kalinga (current Odisha) which end up being the defining moment of his life. The Kalinga war saw awful homicide and annihilation. The sufferings and abominations of the war zone slashed the core of Ashoka. He made a purpose not to take up arms any more. He understood the fiendishness of common victory and the excellence of good and profound victory. He was attracted to the lessons of Buddha and gave his life to the victory of men’s heart by the law of obligation or devotion. He advanced a strategy of Dharma Vijaya, ‘Victory by Piety’.

End of the Mauryan Empire
Ashoka was prevailing by frail rulers, which urged the regions to declare their autonomy. The exhausting assignment of controlling a particularly immense domain couldn’t be executed by the powerless rulers. The shared squabble among the replacements additionally added to the decay of the Mauryan Empire.
In the start of the first century A.D., the Kushanas set up their position over the north-west boondocks of India. The most acclaimed among the Kushana rulers was Kanishka (125 A.D.- 162 A.D.), who was the third in the Kushana administration. The Kushana rule proceeded till the center of third century A.D. The most remarkable accomplishment of their standard was the improvement of Gandhara School of Art and further spread of Buddhism into far off districts of Asia.


Gupta Dynasty

After the Kushanas, the Guptas were the main line. The Gupta time frame has been portrayed as the Golden Age of Indian history. The main well known lord of the Gupta tradition was Ghatotkacha’s child Chandragupta I. He wedded Kumaradevi, the girl of the head of the Licchavis. This marriage was a defining moment in the existence of Chandragupta I. He got Pataliputra in endowment from the Lichhavis. From Pataliputra, he established the framework of his realm and began vanquishing many adjoining states with the assistance of the Licchavis. He controlled over Magadha (Bihar), Prayaga and Saketa (east Uttar Pradesh). His realm reached out from the waterway Ganges to Allahabad. Chandragupta I additionally got the title of Maharajadhiraja (King of Kings) and managed for around fifteen years.
Chandragupta I was prevailing by Samudragupta in around 330 A.D., who ruled for around fifty years. He was an incredible military virtuoso and is said to have directed a military mission across the Deccan, and furthermore repressed the backwoods clans of the Vindhya area.
Samudragupta’s replacement Chandragupta II, otherwise called Vikramaditya, vanquished the broad domains of Malwa, Gujarat and Kathiawar. This gave outstanding abundance, which added to the thriving of the Guptas. The Guptas in this period occupied with ocean exchange with the nations of the west. It was most likely during his rule that Kalidas, the best Sanskrit writer and screenwriter, just as numerous other researcher and researchers thrived.

Decrease of Gupta Dynasty

The decrease of the Gupta power in northern India between the end of fifth and the sixth century A.D. offered ascend to different little autonomous realms and pulled in unfamiliar attacks of Huns. Toramara was the head of the Huns and was effective in attaching huge pieces of the Gupta Empire. His child, Mihirakula was a brutal savage and one of the most exceedingly awful dictators known. Two local ground-breaking sovereigns, Yasodharman of Malwa and Baladitya of Magadha squashed his force and shut down his reign in India.

Harshavardhana

With the initiation of the seventh century, Harshavardhana (606-647 A.D.) rose the seat of Thaneshwar and Kannauj on the demise of his sibling, Rajyavardhana. By 612 Harshavardhana combined his realm in northern India.
In 620 A.D. Harshavardhana attacked the Chalukya realm in the Deccan, which was then governed by Pulakesin II. Yet, the Chalukya obstruction demonstrated intense for Harshavardhana and he was vanquished. Harshavardhana is notable for his strict lenience, capable organization and political relations. He kept up strategic relations with China and sent emissaries, who traded thoughts of the Chinese rulers and built up their insight about one another.
The Chinese voyager, Hiuen Tsang, who visited India during his rule, has given a distinctive portrayal of the social, financial and strict conditions, under the standard of Harsha praises the ruler. Harsha’s passing, indeed, left India with no focal central force.

The Chalukyas of Badami

The Chalukyas were an incredible force in southern India somewhere in the range of sixth and eighth century A.D. Pulakesin I, the principal incredible leader of this line rose the seat in 540 A.D. furthermore, having made numerous amazing triumphs, set up a strong realm. His children Kirtivarman and Mangalesa further expanded the realm by pursuing numerous fruitful battles against the neighbors including the Mauryans of the Konkans.
Pulakesin II, the child of Kirtivarman, was one of the best leader of the Chalukya tradition. He controlled for very nearly 34 years. In this long rule, he combined his clout in Maharashtra and vanquished huge pieces of the Deccan. His most noteworthy accomplishment was his triumph in the guarded battle against Harshavardhana.
Notwithstanding, Pulakesin was crushed and executed by the Pallav ruler Narasimhavarman in 642 A.D. His child Vikramaditya, who was additionally as incredible a ruler as his dad, succeeded him. He restored the battle against his southern adversaries. He recuperated the previous magnificence of the Chalukyas by and large. Indeed, even his incredible grandson, Vikramaditya II was likewise an extraordinary fighter. In 753 A.D., Vikramaditya and his child were ousted by a boss named Dantidurga who established the framework of the following extraordinary domain of Karnataka and Maharashtra called Rashtrakutas.

The Pallavas of Kanchi

In the last quarter of the sixth century A.D. the Pallava lord Sinhavishnu rose to control and vanquished the territory between the streams Krishna and Cauveri. His child and replacement Mahendravarman was an adaptable virtuoso, who lamentably lost the northern pieces of his territory to the Chalukya lord, Pulekesin II. Be that as it may, his child, Narsinhavarman I, squashed the force of Chalukyas. The Pallava power arrived at its great statures during the rule of Narsinhavarman II, who is notable for his design accomplishments. He assembled numerous sanctuaries, and craftsmanship and writing thrived in his occasions. Dandin, the incomparable Sanskrit researcher, lived in his court. Nonetheless, after his demise, the Pallava Empire started to decay and in course of time they were decreased to a simple neighborhood ancestral force. At last, the Cholas crushed the Pallava lord Aparajita and assumed control over their realm towards the end of the ninth century A.D.
The old history of India has seen the ascent and destruction of a few administrations, which have left their heritages actually reverberating in the brilliant book of Indian history. With the finish of the ninth century A.D., the middle age history of India began with the ascent of domains, for example, the Palas, the Senas, the Pratiharas and the Rashtrakutas, etc.

www.GKDuniya.in will update many more new jobs and study materials and exam updates, keep Visiting and share our post of Gkduniya.in, So more people will get this. This content and notes are not related to www.GKDuniya.in and if you have any objection over this post, content, links, and notes, you can mail us at gkduniyacomplaintbox@gmail.com
And you can follow and subscribe to other social platforms. All social site links in the subscribe tab and bottom of the page.
Important Links
Particulars Official Links |
Related Links |
You-tube |
GKDuniya9 |
|
|
GKDuniya.in, IndiaDigitalHub |
|
|
GKDuniya.in |
Another site visit |
Indiadigitalhub.com |

